How do Terpenes Effect the Brain?
When it comes to the effects of terpenes on the brain, they can play a crucial role in modulating the limbic system. The limbic system is a complex network of brain structures involved in several functions including emotions, memory, motivation, and the regulation of several physiological responses. The limbic system plays a crucial role in processing and integrating sensory information and is often referred to as the "emotional brain". It is connected to other parts of the brain and systems of the body and can be accessed consciously through spiritual and meditative practices as well as through cannabis and terpenes.
The key structures of the limbic system include the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
P.S. In order to more fully understand the effects of terpenes on the brain, particularly those found within cannabis, you should first understand what terpenes are and how they effect the body. Please visit the blog titled "Cannabis Terpenes and their Effects on the Body" for a more in depth discussion of plant terpenes.
What is the amygdala?
The amygdala is the part of the brain responsible for processing and regulating emotions, particularly fear and aggression. It is also involved in the storage of emotional memories.
What is the hippocampus?
The hippocampus is the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory formation particularly in the context of spacial memory and long-term memory consolidation. It is the part of the brain most affected by Alzheimer's disease. Scientists have discovered that those affected by this disease exhibit atrophy of the hippocampus. In other words, a shrinking hippocampus is associated with Alzheimer's disease.
What is the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is the area of the brain responsible for regulating various autonomic (think automatic) functions of the body such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep. It also plays a role in activating the endocrine system, a network of glands located throughout the body which release hormones to control and coordinate your body's internal metabolism, growth and development, and energy levels, as well as your body's response to injury, stress, and environmental factors.
What is the thalamus?
The thalamus acts as a relay station for sensory information such as vision, hearing, touch, taste and smell. It regulates states of consciousness and alertness by filtering and prioritizing what reaches your conscious awareness. It relays signals between various sensory pathways and the cerebral cortex, the part of the brain responsible for many higher-order cognitive functions including sensory processing, motor control, perception and consciousness (awareness/focus), social and emotional processing (social cues), and complex problem solving. Overall, the thalamus acts as a relay and integration center, facilitating the flow of sensory information, regulating consciousness and alertness, contributing to motor control, memory, emotional processing, and coordinating interactions among different brain regions. Its intricate connections and interactions with other brain processes and systems are essential for the overall functioning of the central nervous system.
How does PTSD affect the limbic system?
PTSD (post traumatic stress disorder) is caused by unhealed trauma that the body and mind have been unable to fully process. As a result, the limbic system of the body can be triggered, leading to a cascade of physiological responses. Let's dive into how PTSD and its effects have on the body.
If you've ever had a bad experience involving heightened emotions such as fear or aggression (amygdala), the memory of this trauma (hippocampus) can be triggered through sensory input (thalamus) such as an image, smell, sound, taste, place, etc. A change in your breathing pattern occurs resulting in a slow shallow breathing (hypothalamus). This in turn lowers the amount of oxygen in the brain and body which triggers a reaction to fight to stay alive. The adrenal glands (endocrine system), produce adrenaline, which quickens all responses in the body including the heart and lungs (hypothalamus). Your heart pumps faster and your breath quickens. The quickened breathing followed by sweat production then reinforce the negative thought/memory/emotion by creating this mirror of physiological circumstance as when the memory first happened. This negative feedback loop of "reliving the experience" is what those who suffer from PTSD encounter.
Negative feedback loops can happen to anyone. The good news is that you can use higher functioning parts of the brain (cerebral cortex) to help regulate the limbic system by consciously engaging your body and its responses. Changing your pattern of breathing is a good skill to learn regardless of whether or not you suffer from PTSD. Box breathing is an incredible tool that can be implemented whenever the limbic system is triggered and is in a negative feedback loop.
Box breathing in 4 simple steps:
1. Breath in for four counts
2. Hold your breath for four counts
3. Breathe out for four counts
4. Hold your breath for four counts & repeat
This simple yet effective tool can help alleviate negative limbic system responses by putting the mind and body back into a state of homeostasis (balance). Although cannabis can also help alleviate these negative responses, strengthening the body's naturally systems and processes should be your first line of defense. Doing this and other meditative practices with certified pure therapeutic grade essential oils can help curb and protect against habitual cannabis use. When all else fails, cannabis and its terpenes can be used as a medicine to help alleviate the circuitry in the brain that has gone haywire.
Plant terpenes, including those found in cannabis, have the potential to affect the limbic system through various mechanisms. Here are a few ways in which terpenes can potentially influence the limbic system:
Neurotransmitter modulation: Terpenes can interact with neurotransmitter systems, such as serotonin, dopamine, and GABA, which are involved in emotional regulation, reward, and mood. By modulating these neurotransmitters, terpenes may impact the functioning of the limbic system and influence emotions and mood states.
Olfactory (smelling) stimulation: Inhalation of terpenes, either through the aroma of plants or the use of essential oils, can stimulate the olfactory system. The olfactory system has direct connections to the limbic system, allowing the odor molecules to activate the limbic structures and potentially influence emotional states and memories.
Pharmacological effects: Some terpenes may have direct pharmacological effects that can influence the limbic system. For example, certain terpenes have shown anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) or sedative properties, which could impact the functioning of the limbic system involved in emotional regulation and arousal.
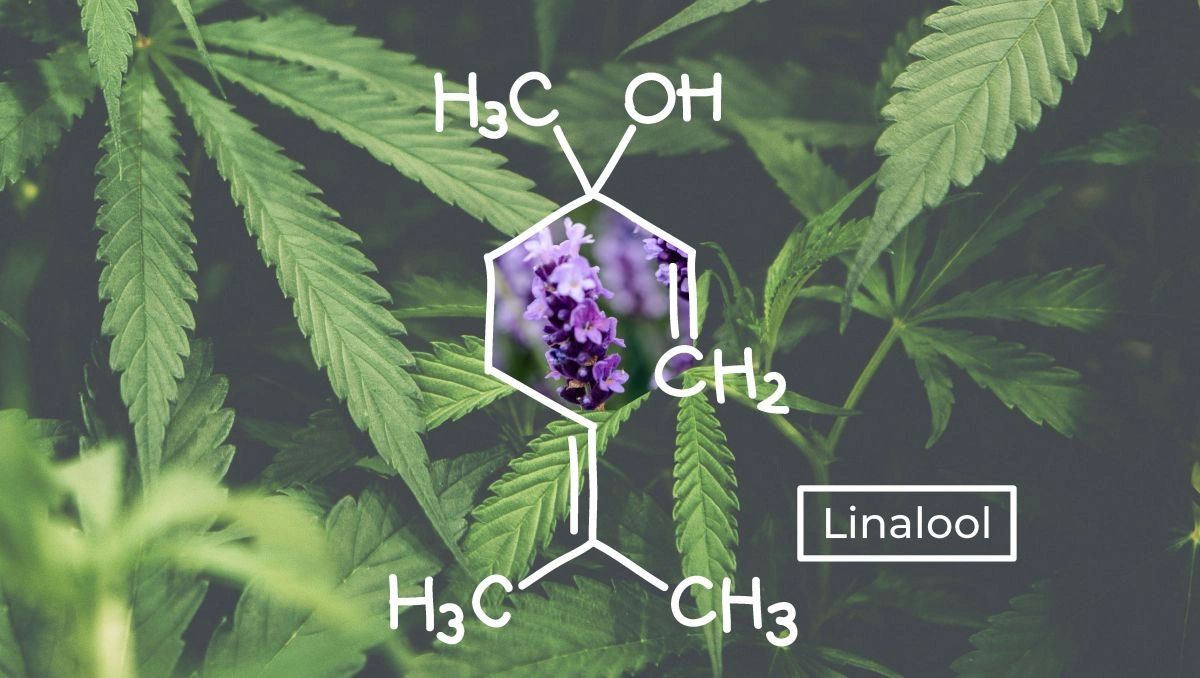
When it comes to cannabis terpenes, the "entourage effect" is perhaps the most therapeutic. In fact, when most people use cannabis and feel the calming effects within seconds, what they're actually witnessing are the terpenes within cannabis. This is because cannabinoids can take a few minutes to up to an hour to kick in depending on whether the medicine is inhaled (smoked/vaped) or eaten (edibles). To increase the entourage effect to another level of healing, using cannabis with certified pure therapeutic grade essential oils can be an incredible way of introducing other plant terpenes for full body recovery and healing.
Plant terpenes help heal the body and mind. By helping modulate the limbic system functions, terpenes can help the body enter into a space of grace, peace, and acceptance. In this space of peace and acceptance the body enters homeostasis, a state of balance. It is in this place of balance, that the body can repair itself and heal more rapidly.
P.S. Remember to use the discount code: ASA5 at checkout for 5% off your entire order.
Asa


