THC and its derivatives
The human body is an amazing machine with incredible potential. The body has systems and processes that work together to achieve balance, called homeostasis. One of these systems which helps in homeostasis is the endocannabinoid system (ECS). It plays a key role in regulating several physiological processes including pain, appetite, mood, and immune function. The endocannabinoid system has tiny receptors that are found on the surface of cells in various parts of the body. These receptors act as doorways which can only be opened with special “keys” known as cannabinoids.
There are two types of cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2. While CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, CB2 receptors are mostly located in the immune system and surrounding tissue such as the bone marrow, gastrointestinal track, and spleen. Both CB1 and CB2 receptors can be activated by cannabinoids, which the body can either produce endogenously (produce on its own) in the form of anandamide and adenosine, or by utilizing the over 100 cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant. To put it simply, the endocannabinoid system helps the human body regulate its processes and achieve homeostasis and cannabis can be used as a plant medicine to help create that harmonious balance. Although there are over 100 cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant, science has studied only a handful. Here we will go over the cannabinoids which primarily effect the CB1 receptors and which produce the "high" someone may feel when using them.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
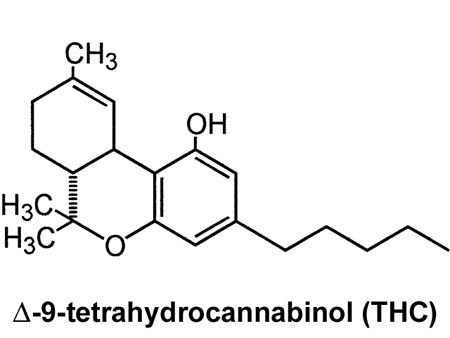
THC ( ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol)
THC otherwise known as delta-9-tetrahydrocannibinol or simply delta-9, is the main psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. ∆9 binds to the CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system causing a range of effects such as altered perception, euphoria, relaxation, and appetite aka “the munchies”. In moderate to high doses it can cause negative side effects such as anxiety and paranoia. These deep-seated side effects are actually caused by unhealed parts of the ego. As perceptions are altered, the ego senses a loss of control and fights to stay in control. The more the ego fights, the more anxious or paranoid a person may feel. On a deeper and more spiritual level, THC is believed by some to be a spiritual medicine, which, can help us look deeper within ourselves, heal our wounded parts, and accept that control is just an illusion.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
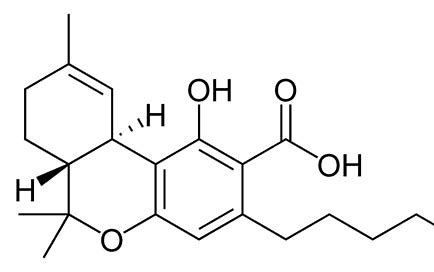
TCHa (tetrahyrocannibinolic acid)
Most of the THC in cannabis is actually found in the non-psychoactive cannabinoid called THCa, or tetrahyrocannibinolic acid. THCa is not psychoactive because it does not directly bind to the CB1 receptors in the brain, and because THCa is not psychoactive, it is not regulated as a controlled substance. THCa has been shown to be anti-inflammatory (reduces inflammation), neuro-protective (protects the nervous system from injury and damage), anti-emetic(i.e. nausea inhibiting), and anti-proliferative (anti-cancer).
The chemical process to convert THCa into THC is called decarboxylation. Decarboxylation occurs naturally over time as cannabis is directly exposed to UV light, dries, and ages. Decarboxylation can also be expedited by heating the plant material. When cannabis is heated, such as when it is smoked or vaporized, the heat causes the carboxyl group (-COOH) to break off from the cannabinoid molecule, resulting in THC, the psychoactive form of the compound. Another way to think of THCa is as a key that doesn’t quite fit into the CB1 receptor lock, because it has an extra tooth on the key. When THCa is heated, this extra tooth is removed allowing it to fit into the CB1 receptor lock and give the desired effects of THC. Interestingly, the -COOH metabolite is what many marijuana drug tests are testing for and can stay in the body for several weeks. This decarboxylation process is important when preparing edibles, tinctures, or other infused products, as it ensures that all the cannabinoids are in their active forms to give the desired effects.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the most psychoactive cannabinoid, THC, and its non-psychoactive precursor, THCa, we can now look at its analogs that either occur naturally or are synthesized in the lab.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
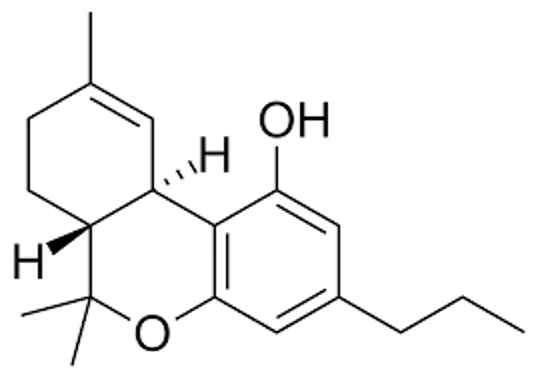
THCV (tetrahydrocannabivarin)
THCV was first discovered in 1973 and has a 3-term chain as compared with THC which has a 5-term chain. THCV is referred to as a homolog of THC and as such it has a different biological effect on the body because it does not bind to CB receptors as strongly. It is important to note that a minimum of 3 carbon atoms is required to bind to both the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Generally speaking the more carbon atoms a THC analog has, the more potential binding ability it has.THCV acts as an antagonist of the CB1 receptor at low doses meaning it has the opposite effect of THC. In high doses however it acts as an agonist of the CB1 receptor meaning it produces the reaction that is typical for that substance (THC). THCV is therefore both an antagonist and agonist of the CB1 receptors depending on its non-psychoactive low dose use and psychoactive high dose use. THCV is most well-known for its appetite suppressant effect and has been studied for treating type 2 diabetes. THCV is also used as an anti-fatigue medicine giving you more energy with the added benefit of also being an appetite suppressant which leads to weight loss.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
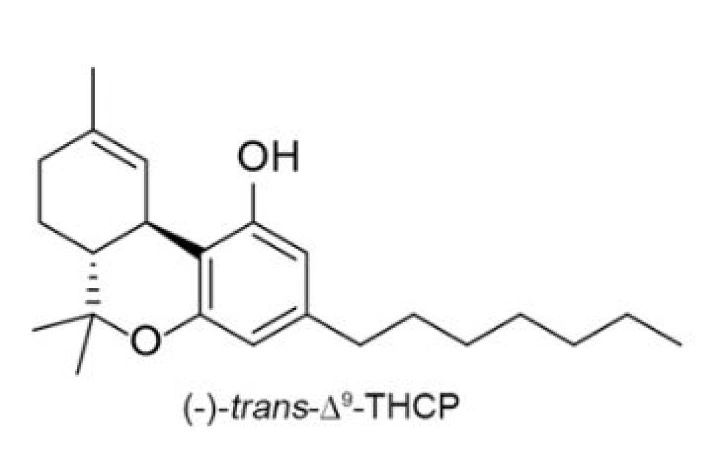
THCP (tetrahydrocannabiphorol)
Discovered in 2019, THCP has been the most recently discovered cannabinoid originally found in the Italian FM2 cannabis strain. It is a special type of analog called a homolog in that it belongs to a series of compounds differing from one another by a repeating unit. As delta 9 THC has a 5-term alkyl side chain meaning there are 5 carbon atoms in the side chain alkyl group, THCP has a 7-term alkyl side chain.
Since THCP has 7 carbon atoms, it binds 33 times stronger than delta 9 THC’s binding ability. As such it is much more potent than any other naturally occurring psychoactive cannabinoid. The medical benefits of THCP are currently unknown.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
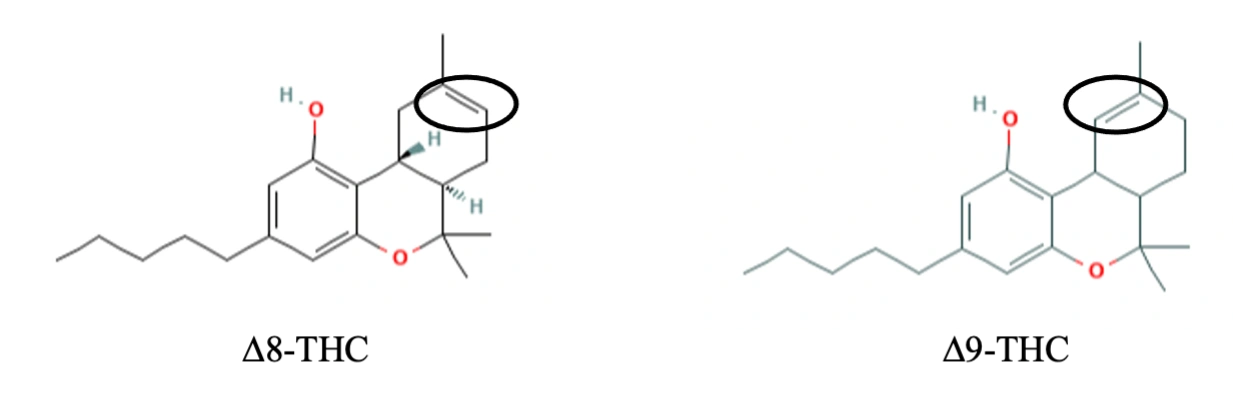
∆8 THC (delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol)
Delta 8 THC was first discovered in the 1970’s and has been the subject to a number of clinical tests and proven medical utility. Delta 8 THC is about half as psychoactive as delta 9 THC and is an isomer. An isomer is a compound that contains the same number of atoms but differs in its structural arrangement and properties. The only structural difference between Delta 8 and Delta 9 THC is the placement of the double bond, yet the effects on the body are quite different. Delta 8 THC’s main medical benefit is that it is an anti-emetic (anti-nausea) that can be used for pediatric chemotherapy cancer patients without the stronger psychoactive effects associated with delta 9 THC. It has grown in popularity as an anti-anxiety and relaxing medicine as well.
 Edit Image
Edit Image
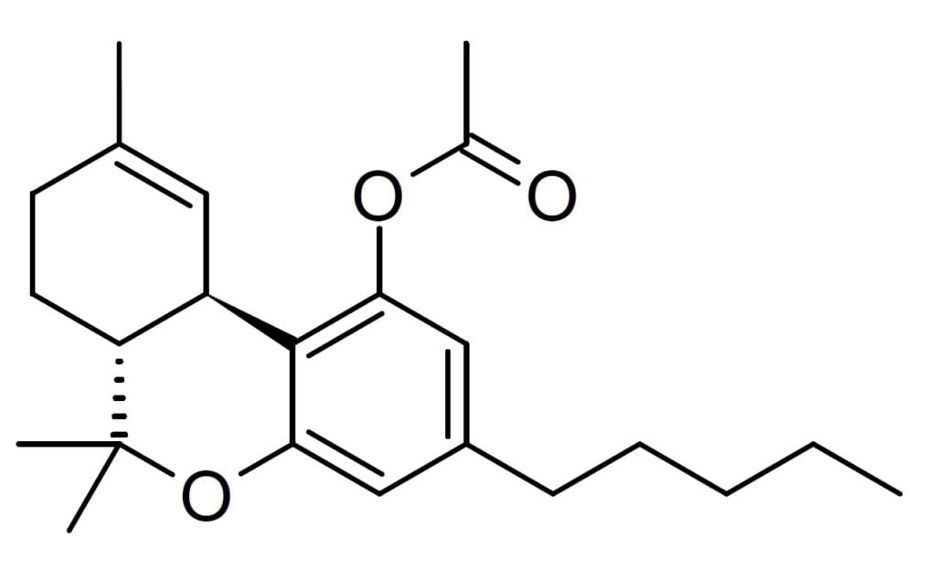
THC-O Acetate
THCO is a new synthetic, non-natural cannabinoid with psychoactive effects. According to studies and consumer feedback THC-O (THCO) can be as much as 3x more potent than delta-9 THC and some report it as having a more spiritual tone. THC-O is gaining popularity among users and researchers but because this cannabinoid is not found naturally in the hemp plant like other cannabinoids such as THC, THCV, delta-9 THC, CBD, CBG, CBN, etc. its legal status is a little shaky.
The DEA is closely monitoring THC-O, THC-P, delta-8-THC, and other synthetically produced cannabinoids as the 2018 federal farm bill does not affect “the control status of synthetically derived tetrahydrocannabinols because hemp, as defined by the statue, is limited to materials that are derived from the plant cannabis sativa L.” It also states, “all synthetically derived tetrahydrocannabinols remain schedule I controlled substances.” 85 Fed. Reg. at 51,641. This language suggests the source of the product, not the method of manufacture, is the dispositive factor for ascertaining whether a product is synthetic. A recent agency letter bolsters this understanding. There, the DEA clarifies that “synthetic” delta-8 THC that is produced “from non-cannabis materials” remains banned.
In other words, as long as these synthetic THC derivatives are produced from hemp plant material, they remain federally legal in all 50 states under the 2018 federal farm bill. The definition of hemp is any cannabis plant at the time of harvest that is under 0.3% THC by dry weight. Plants over this 0.3% THC limit are classified as "marijuana" and any products produced from this "hot" material are thereby federally illegal as schedule 1 drugs, despite many states adopting their own medical or recreational marijuana legal status. It would seem that any power the DEA thinks it has or tries to grab over hemp and any of its derivatives is null and void as it would be an encroachment of the people's liberties and an overstep of their actual powers and duties. One could argue that any of the states enacting their own hemp laws could also be considered an erosion of liberties, because hemp is federally legal, and criminalizing a plant that is federally legal makes constituents wonder.. "why the fuss?" One underlying reason some states are enacting their own laws regarding hemp is because it directly competes with their campaign contributors (i.e. pharmaceutical drug companies), their medical marijuana stores/programs, or their alcohol sales if you're in Utah (Utah state owns the liquor stores in Utah). Time will tell if legislators, and those that support them, will continue to derive their cheap moral virtue by enacting unjust laws that demonize a plant who's only purpose is to help us heal.
Our products use THC and derivatives derived from hemp, which are federally legal under federal law, and can be purchased without a medical card and shipped right to your front door through the United States Postal Service!
Asa,
P.S. You can use discount code: ASA5, for 5% off your entire order every time you order from our site. This is just a little way of saying thank you for educating yourself.


